The severe form of gum disease known as periodontitis can be a real pain in the neck. The good news is that this problem can be treated, and your oral health restored. In this article, we’ll discuss periodontitis, its symptoms, and the therapies available to help you.
Understanding Periodontitis
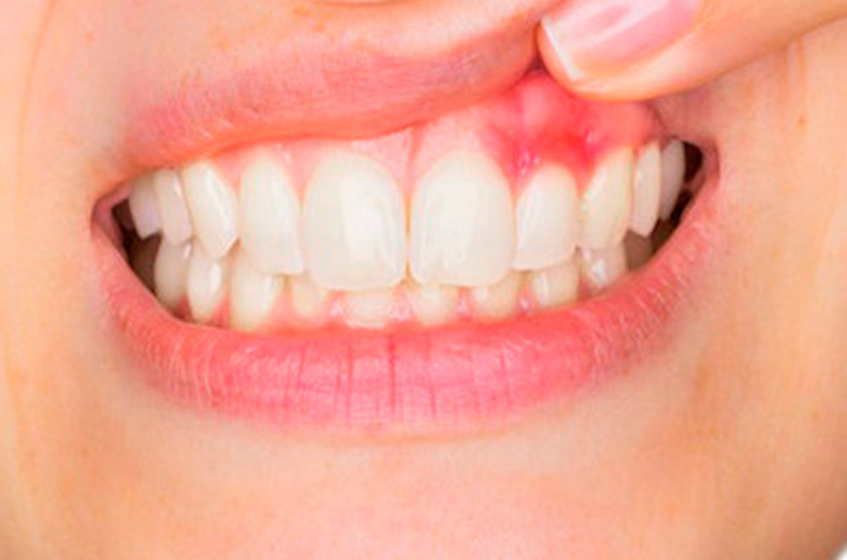
Periodontitis, often known as gum disease, is an infection of the gums and bones that hold your teeth in place. Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease, characterized by gum redness, swelling, and bleeding. Gingivitis, if left untreated, can develop into periodontitis, which can cause gum recession, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Periodontitis
Fortunately, several treatments can assist in controlling and reducing periodontitis symptoms. These treatments aim to remove the infection in gum tissues and prevent further damage to the teeth and supporting structures.
Scaling and Root Planing
This non-surgical procedure involves deep cleaning the teeth and their roots. Expert dentists use specialized devices to scrape tartar and plaque off teeth roots. This therapy encourages gum tissue recovery by removing the infection’s cause.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection. The severity of the disease determines whether the antibiotics should be taken orally or given topically.
Laser Therapy
Laser technology is increasingly used to treat periodontitis. It can help regenerate gum tissue by removing infected tissue and bacteria.
Surgical Procedures
For advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical interventions may be necessary. Gum and bone damage can be repaired using techniques such as flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration.
Maintenance and Ongoing Care
After treatment, it’s crucial to maintain regular dental check-ups and cleanings. This permits your dental health to be monitored and ensures the disease does not reoccur.
The Link Between Oral Bacteria and Health Risks
Periodontitis has been connected to several systemic health risks in addition to its effects on your oral health. Recent studies have suggested a link between oral bacteria and brain abscesses, highlighting the importance of treating gum disease promptly.
Inflamed gum tissue is a portal through which oral bacteria can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. While this is uncommon, they highlight the need to address periodontitis for both dental and general health.
Prevention is Key
Avoiding periodontitis altogether is preferable to fixing the problem afterwards. Good oral hygiene habits, which can lower the likelihood of gum disease, include:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Regularly visit your dentist for check-ups and cleanings.
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption, as these habits can contribute to gum disease.
In conclusion, if you find yourself frustrated by periodontitis, know that there are effective treatments available to address this condition. If you have oral problems, you should immediately consult a dentist to avoid complications.
In addition, avoiding gum disease altogether requires good dental hygiene routines. Taking good care of your teeth and gums might prevent severe conditions like brain abscesses caused by oral germs.